Wyszukaj w publikacjach
Zespół posturalnej tachykardii ortostatycznej (POTS) – co powinien wiedzieć lekarz POZ?
Zespół posturalnej tachykardii ortostatycznej (POTS) to zaburzenie układu autonomicznego, charakteryzujące się nadmiernym wzrostem częstości akcji serca podczas pionizacji, prowadzącym do szeregu objawów klinicznych, które ustępują po przyjęciu pozycji leżącej.
Definicja i kryteria diagnostyczne POTS
POTS definiuje się jako wzrost częstości akcji serca o co najmniej 30 uderzeń na minutę (lub przekroczenie 120 uderzeń na minutę) w ciągu 10 minut od przyjęcia pozycji stojącej, bez towarzyszącej hipotensji ortostatycznej. Objawy te muszą utrzymywać się przez co najmniej 6 miesięcy i nie mogą być wynikiem innych schorzeń.
Epidemiologia POTS
POTS dotyka głównie kobiet w wieku od 15 do 50 lat, choć może dotyczyć każdej grupy wiekowej. Szacuje się, że częstość występowania wynosi od 0,1% do 1% populacji.
Etiologia i patofizjologia POTS
Etiologia POTS nie została jeszcze w pełni poznana. Wśród potencjalnych przyczyn wymienia się:
- nadmierną aktywność układu współczulnego – prowadzącą do zwiększonego uwalniania norepinefryny;
- neuropatię autonomiczną – uszkodzenie nerwów odpowiedzialnych za regulację napięcia naczyń krwionośnych;
- zaburzenia autoimmunologiczne – obecność autoprzeciwciał przeciwko receptorom adrenergicznym i cholinergicznym.
W wyniku tych mechanizmów dochodzi do nieadekwatnej odpowiedzi układu krążenia na pionizację, co skutkuje nadmiernym wzrostem częstości akcji serca w celu utrzymania perfuzji narządowej.
Postać różni się od postępującego niedociśnienia ortostatycznego większym wzrostem częstości akcji serca i mniejszym spadkiem ciśnienia krwi.
Objawy kliniczne POTS
Objawy ortostatyczne
- zawroty głowy lub uczucie lekkości,
- kołatanie serca,
- stan przedomdleniowy,
- zaostrzenie objawów pod wpływem ciepła.
Objawy nieortostatyczne
Rozlane objawy towarzyszące
- zmęczenie,
- zaburzenia snu,
- migrenowy ból głowy,
- ból mięśniowo-powięziowy.
Objawy, których doświadczają pacjenci z POTS, różnią się od objawów pacjentów z niedociśnieniem ortostatycznym, ponieważ występują znaczące objawy aktywacji współczulnej.
Diagnostyka POTS
Rozpoznanie POTS powinno opierać się na:
- wywiadzie:
- ocena nasilenia i czasu trwania objawów ortostatycznych (np. zawroty głowy, kołatanie serca, uczucie osłabienia po wstaniu);
- identyfikacja czynników wyzwalających i nasilających objawy (np. wysiłek fizyczny, ciepło, posiłki, menstruacja);
- ocena wpływu objawów na czynności dnia codziennego – praca, szkoła, codzienne obowiązki;
- przegląd objawów innych układów w celu wykrycia możliwej neuropatii autonomicznej (np. zaburzenia pocenia, objawy ze strony układu pokarmowego i moczowego);
- dokumentacja objawów towarzyszących (zmęczenie, zaburzenia snu, migrena, nietolerancja wysiłku);
- pytania o choroby współistniejące (np. zespół przewlekłego zmęczenia, zespół Ehlersa-Danlosa, choroby autoimmunologiczne);
- badania i testy diagnostyczne w POTS:
| Test | Wynik diagnostyczny | Komentarz |
|---|---|---|
Test pochyleniowy (HUT – head-up tilt) | tachykardia ortostatyczna bez spadku ciśnienia, reprodukcja objawów | złoty standard diagnostyczny |
Katecholaminy w osoczu (na leżąco i na stojąco) | ↑ noradrenalina przy pionizacji (>600 pg/ml sugeruje podtyp hiperadrenergiczny) | pomaga w ustaleniu podtypu POTS |
Badania laboratoryjne | niedokrwistość, zaburzenia elektrolitowe, choroby tarczycy, nieprawidłowości hormonów nadnerczy, podwyższone stężenie katecholamin i ich metabolitów we krwi i moczu | umożliwiają diagnostykę różnicową |
Manewr Valsalvy | nadmierne podwyższenie ciśnienia tętniczego i tętna | może być stosowany jako test potwierdzający; sugeruje również obecność „hiperadrenergicznego” typu POTS |
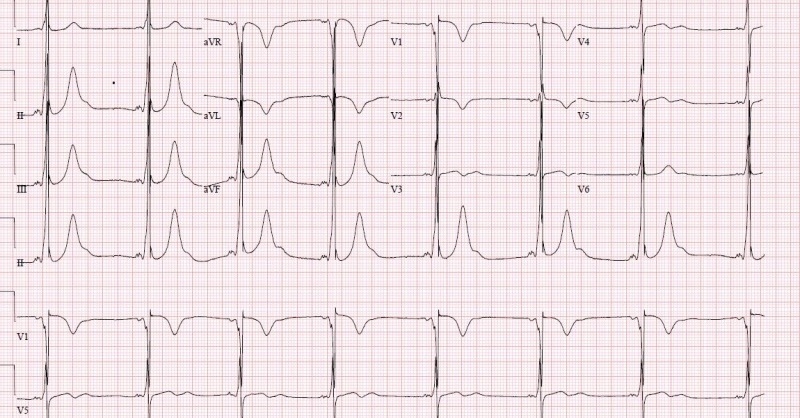
EKG spoczynkowe | wykluczenie arytmii i zmian strukturalnych | badanie przesiewowe |
ECHO serca i Holter EKG (24–48h) | ocena struktury serca i rytmu, tachykardia dzienna, brak spadku tętna w nocy | pomaga różnicować POTS z innymi zaburzeniami rytmu |
Screening odruchów autonomicznych | zaburzenia odruchów ciśnienia/tętna/potliwości | wskazuje na neuropatyczny podtyp |
Test wysiłkowy (EKG + tolerancja wysiłku) | nietolerancja wysiłku, nieprawidłowe reakcje hemodynamiczne | ocena sprawności i reakcje sercowo-naczyniowe |
Oznaczanie przeciwciał (np. przeciwko receptorom adrenergicznym, muskarynowym) | ich obecność może sugerować autoimmunologiczne POTS | rzadziej wykonywane, ale istotne w podtypie autoimmunologicznym |
W diagnostyce różnicowej należy wykluczyć inne przyczyny tachykardii, takie jak:
- nadczynność tarczycy,
- anemia,
- odwodnienie,
- zaburzenia lękowe,
- ból,
- infekcje,
- leki (sympatykomimetyki, leki antycholinergiczne),
- guz chromochłonny.
Leczenie POTS
Heterogeniczność i szerokie spektrum objawów związanych z POTS stanowią duże wyzwanie dla lekarzy i dotkniętych chorobą pacjentów. Ponadto, słabo zbadana patofizjologia POTS sprawia, że leczenie przyczynowe choroby nie jest możliwe, a interwencje zwykle koncentrują się na łagodzeniu objawów.
Metody niefarmakologiczne
- Zwiększenie spożycia soli i płynów – w celu zwiększenia objętości krwi krążącej (min. 2,5 l płynów i suplementacja sodu).
- Noszenie pończoch uciskowych – zmniejsza zaleganie krwi w kończynach dolnych (zalecana klasa 2 ucisku).
- Regularna aktywność fizyczna – trening aerobowy i oporowy, początkowo w pozycjach półleżących, poprawia tolerancję ortostatyczną.
- Zmiana stylu życia i edukacja pacjenta – unikanie długiego stania, wysokiej temperatury, duże posiłki zastąpione mniejszymi, stopniowe wstawanie, fizyczne kontrmanewry (skrzyżowanie nóg, napinanie mięśni).
Metody farmakologiczne
- Leki kontrolujące tętno:
- β-blokery (np. propranolol, metoprolol) – zmniejszają częstość akcji serca; szczególnie skuteczne w podtypie hiperadrenergicznym z tachykardią ortostatyczną;
- iwabradyna – alternatywa dla β-blokerów, szczególnie przy niskim ciśnieniu lub ich nietolerancji;
- werapamil – może być stosowany przy wysokim ciśnieniu, migrenie lub bólu w klatce piersiowej, ale dowody na jego skuteczność są ograniczone.
- Leki zwiększające objętość i ciśnienie krwi:
- fludrokortyzon – mineralokortykoid zwiększający retencję sodu i objętość osocza; zalecany w podtypie hipowolemicznym;
- midodryna – agonista receptorów α1-adrenergicznych; podnosi ciśnienie i zmniejsza objawy ortostatyczne, szczególnie w POTS z niskim ciśnieniem;
- klonidyna – zmniejsza aktywność współczulną; zalecana w podtypie hiperadrenergicznym z nadciśnieniem ortostatycznym;
- pirydostygmina – stosowana w przypadku podejrzenia neuropatycznego POTS i objawów ze strony układu pokarmowego;
- desmopresyna – zwiększa retencję wody; może zmniejszyć nykturię, ale skuteczność jest niepewna; (dowody na skuteczność ograniczone);
- ostra infuzja soli fizjologicznej (1–2 l/dzień przez 3–5 dni) – stosowana w ciężkich, zdekompensowanych przypadkach POTS, zwykle w warunkach szpitalnych.
Źródła
- Grubb, B. P., & Karas, B. (2008). Postural tachycardia syndrome: Concepts and management. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19(1), 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8167.2008.01407.x
- Fedorowski, A. (2015). Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: Clinical presentation, aetiology and management. Journal of Internal Medicine, 277(4), 352–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12852
- Brignole, M. (2007). The syndromes of orthostatic intolerance. e-Journal of the ESC Council for Cardiology Practice, 6(5). Retrieved from https://www.escardio.org/Journals/E-Journal-of-Cardiology-Practice/Volume-6/The-syndromes-of-Orthostatic-Intolerance-Title-The-syndromes-of-Orthostatic-I
- Sheldon, R. S., Grubb, B. P., Olshansky, B., Shen, W. K., Calkins, H., Brignole, M., ... & Raj, S. R. (2015). 2015 Heart Rhythm Society Expert Consensus Statement on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Postural Tachycardia Syndrome, Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia, and Vasovagal Syncope. Circulation, 132(4), 115–125. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.144501