Wyszukaj w publikacjach
Współistnienie przewlekłej choroby żylnej z chorobą tętnic obwodowych
Przewlekła choroba żylna (CVD, chronic venous disease) i choroba tętnic obwodowych (PAD, peripheral arterial disease) często współistnieją, co wynika ze wspólnego patomechanizmu chorób naczyń tętniczych i żylnych. Diagnostyka obu schorzeń jest stosunkowo prosta – rozpoznanie CVD i PAD można postawić w oparciu o dokładne badanie podmiotowe i przedmiotowe. Identyfikacja wymienionych schorzeń jest istotna z uwagi na możliwość wczesnego wdrożenia leczenia, co wpływa na poprawę rokowania.
Glikokaliks – funkcja ochronna i następstwa uszkodzenia
Patologie naczyń tętniczych i żylnych mają źródło w zmianach w mikrokrążeniu, które stanowi dominującą część układu naczyniowego. Pierwszym etapem uszkodzenia śródbłonka naczyniowego jest uszkodzenie glikokaliksu w naczyniach tętniczych i żylnych. Glikokaliks jest strukturą o złożonej budowie, składającą się przede wszystkim z białek i glikozaminoglikanów, wyścielającą komórki śródbłonka naczyń tętniczych i żylnych. Jest naładowany ujemnie i silnie uwodniony, składa się z różnych cząsteczek glikozaminoglikanów, takich jak siarczan heparanu, kwas hialuronowy i siarczan chondroityny oraz rdzeni białkowych, do których glikozaminoglikany są przytwierdzone.
Złożona budowa glikokaliksu warunkuje pełnienie przez niego licznych funkcji istotnych dla prawidłowego funkcjonowania śródbłonka. Zasadnicza rola tej struktury polega na mechanicznej ochronie komórek śródbłonka przed czynnikami powodującymi ich fizyczne uszkodzenie, do których zalicza się cząsteczki cholesterolu o niskiej gęstości, płytki krwi oraz komórki zapalne. Glikokaliks pełni funkcję buforu i stanowi barierę, której pory blokują przenikanie dużych składników krwi. Jego elementy proteoglikanowe przenoszą informacje o warunkach przepływu krwi do wnętrza komórki śródbłonka, łącząc się z jego cytoszkieletem. Komórki śródbłonka wykazują zdolność do reagowania na zmiany sił hemodynamicznych i zmiany biochemiczne przepływającej krwi, między innymi poprzez uwalnianie substancji wazoaktywnych, w tym tlenku azotu rozszerzającego naczynia krwionośne [1, 2].
Epidemiologia i patofizjologia przewlekłej choroby żylnej i choroby tętnic obwodowych
W metaanalizie 32 badań obejmującej ponad 300 000 pacjentów wykazano następującą częstość występowania poszczególnych stadiów CVD – C0S: 9%, C1: 26%, C2: 19%, C3: 8%, C4: 4%, C5: 1%, C6: 0,4% [3]. W badaniu przeprowadzonym w polskiej populacji wykazano, że CVD występowała u 46% kobiet i 37% mężczyzn zgłaszających się do lekarza, niezależnie od przyczyny wizyty [4]. W ankietowym badaniu występowanie uczucia ciężkości w obrębie kończyn dolnych podawało 62% ankietowanych, obecność bólu kończyn dolnych zgłaszało 37% badanych, a co trzeci uczestnik zgłaszał obrzęki kończyn dolnych. Objawy podmiotowe były także znacznie częstsze w grupie pacjentów, u których stwierdzano obecność żylaków kończyn. Wśród tych chorych aż 79% podawało występowanie uczucia ciężkości i zmęczenia kończyn dolnych, 57% dolegliwości bólowe, a aż 52% występowanie obrzęku po długim staniu i siedzeniu [5]. W badaniu Bonn Vein Study, u 49,1% mężczyzn i 62% kobiet populacji ogólnej występowały objawy podmiotowe przewlekłych chorób żył, takie jak uczucie ciężkości kończyn, bóle, skurcze czy też uczucie obrzęku [6].
Częstość występowania PAD u osób dorosłych wynosi ok. 12% i jest podobna u kobiet i mężczyzn [7]. Wykazano, że wraz z wiekiem odsetek osób chorujących na PAD zwiększa się. Choroba ta występuje u 20% osób powyżej 70. r.ż. W badaniu SHEP (Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program), obejmującym pacjentów w podeszłym wieku z nadciśnieniem tętniczym, częstość występowania PAD wynosiła 25% wśród mężczyzn oraz 23% wśród kobiet [8].
W The Gutenberg Health Study (GHS) w grupie 12 423 badanych w wieku 40-80 lat oceniono populację pacjentów z CVD. Wykazano, że pacjenci z CVD w stadium zaawansowania C3-C6 stanowili 41% badanych. Zaobserwowano, że im wyższy stopień zaawansowania choroby (od C0 do C6), tym wyższy odsetek występowania otyłości, nadciśnienia tętniczego i dyslipidemii, czyli schorzeń sercowo-metabolicznych, które są klasycznymi czynnikami ryzyka rozwoju miażdżycy [9].
W omawianym badaniu udowodniono także wpływ CVD na rokowanie długoterminowe. W obserwacji 8-letniej potwierdzono niekorzystny wpływ CVD na śmiertelność z przyczyn ogólnych – im wyższe stadium zaawansowania CVD, tym większe ryzyko zgonu. Ponadto wykazano, że gorzej rokowali pacjenci z objawową niż bezobjawową CVD [9].
Ammerman i wsp. [10] ocenili częstość występowania CVD u pacjentów z rozpoznanym PAD, u których wykonywano rezonans magnetyczny. U 21% pacjentów z PAD występowała także CVD. Pacjenci, którzy mieli PAD i CVD, częściej byli otyli i częściej występowała u nich cukrzyca niż u pacjentów tylko z PAD. Ponadto, u pacjentów z towarzyszącą chorobą układu żylnego częściej niż u pacjentów z prawidłowym układem żylnym odnotowano PAD w IV stopniu zaawansowania (57% vs 34%, p=0,0018) [10].
Zmiany patofizjologiczne obserwowane w ścianie niewydolnych żył mają charakter makroskopowy i mikroskopowy. W warstwie środkowej ściany naczynia żylnego dochodzi do zmian strukturalnych polegających na zmniejszeniu masy mięśniowej i zwiększeniu masy komórek zrębu. W naczyniach żylnych dochodzi także do zaburzenia czynności mięśni gładkich, scieńczenia błony środkowej, zastąpienia mięśni gładkich włóknami kolagenu, co wraz z aktywnym stanem zapalnym prowadzi do trwałej zmiany struktury naczyń żylnych [11]. Wymienione wyżej zmiany skutkują obniżeniem napięcia (tonusu) żylnego, refluksem żylnym oraz nadciśnieniem żylnym.
Warto podkreślić, że kaskada procesów przebudowy naczyniowej rozpoczyna się, zarówno w naczyniach tętniczych, jak i w naczyniach żylnych, od uszkodzenia glikokaliksu. Glikokaliks jest złożoną strukturą wyścielającą nabłonek pełniącą liczne funkcje ochronne. Uszkodzenie glikokaliksu zaburza integralność śródbłonka, odsłania struktury inicjujące procesy trombogenne oraz powoduje wzrost przepuszczalności naczyń. Glikokaliks uszkadzają czynniki takie jak:
- wiek,
- niedostateczna aktywności fizyczna,
- nikotynizm,
- nadmierna masa ciała,
- zaburzenia metaboliczne.
Są to czynniki wspólne dla rozwoju PAD i CVD.
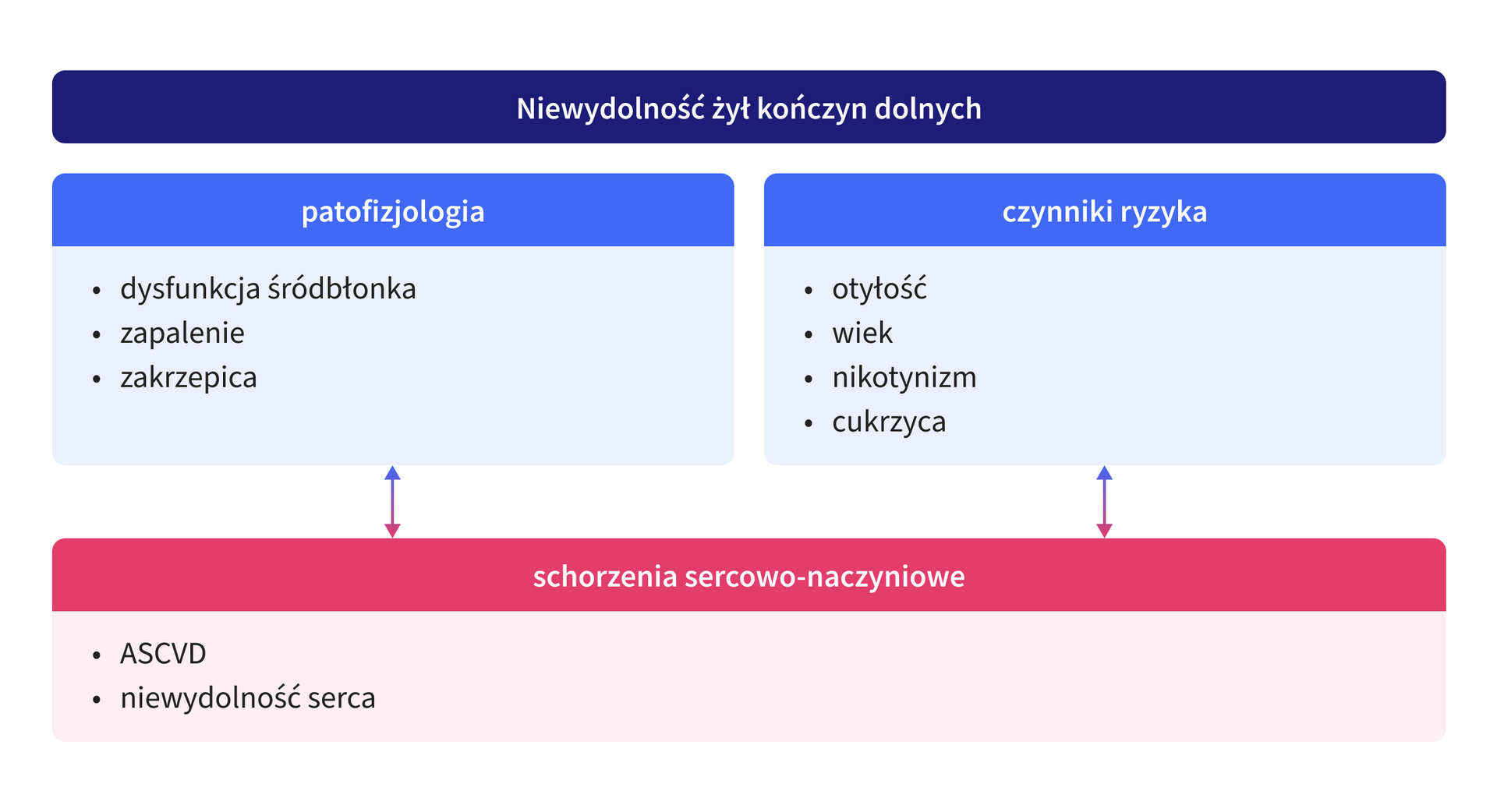
Rycina 1. Związek między chorobami naczyń żylnych i tętniczych.
ASCVD – atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, choroby sercowo-naczyniowe o podłożu miażdżycowym
Diagnostyka przewlekłej choroby żylnej i choroby tętnic obwodowych
PAD może przybierać różne manifestacje kliniczne i przebiegać jako:
- bezobjawowy PAD,
- przewlekły objawowy PAD,
- przewlekłe zagrażające kończynie niedokrwienie (CLTI, chronic limb-threatening ischemia),
- ostre niedokrwienie kończyny (ALI, acute limb ischemia).
Pacjenci z PAD mają różne nasilenie objawów klinicznych, w zależności od zaawansowania choroby, schorzeń współistniejących i stosowanego leczenia. Wymienione postacie PAD mogą ulegać progresji lub regresji w zależności od naturalnego przebiegu choroby i podejmowanego leczenia [11]. PAD należy aktywnie poszukiwać w grupach pacjentów wymienionych w tabeli 1.
Tabela 1. Grupy pacjentów ze zwiększonym ryzykiem choroby tętnic obwodowych [11].
| Zwiększone ryzyko wystąpienia PAD |
|---|
wiek ≥65 lat |
wiek 50-64 lata + jeden z poniższych: - czynniki ryzyka miażdżycy (DMT2, nikotynizm, dyslipidemia, nadciśnienie tętnicze) - CKD - PAD w rodzinie |
wiek <50 lat + DMT2 + dodatkowy czynnik ryzyka miażdżycy |
pacjenci z miażdżycą w innych naczyniach (wieńcowych, szyjnych, nerkowych, AAA) |
AAA – abdominal aortic aneurysm, tętniak aorty brzusznej; CKD – chronic kidney disease, przewlekła choroba nerek; DMT2 – diabetes mellitus, cukrzyca typu 2; PAD – peripheral arterial disease, choroba tętnic obwodowych
CVD także może manifestować się na różne sposoby. Należy podkreślić, że u pacjentów z CVD charakter odczuwalnych dolegliwości jest subiektywny. Brak jest liniowej korelacji objawów ze stopniem zaawansowania klinicznego przewlekłych chorób żył [12]. Obecnie najczęściej stosowana jest klasyfikacja oceny klinicznej zaawansowania CVD – klasyfikacja CEAP, poza oceną objawów przedmiotowych w zakresie parametru C (zaawansowanie kliniczne), zwraca uwagę na możliwości występowania objawów podmiotowych (deskryptor „s”), w każdej ze zdefiniowanych klas C (C0-C6). Zgodnie z ostatnią modyfikacją powyższej klasyfikacji, do dotychczas proponowanych sześciu stopni zaawansowania CVD dodano kolejne deskryptory, w tym: C2r, C4c oraz C6r, odnoszące się odpowiednio do obecności żylaków nawrotowych, zmian o charakterze corona phlebectatica oraz nawrotowych owrzodzeń żylnych podudzi [12].
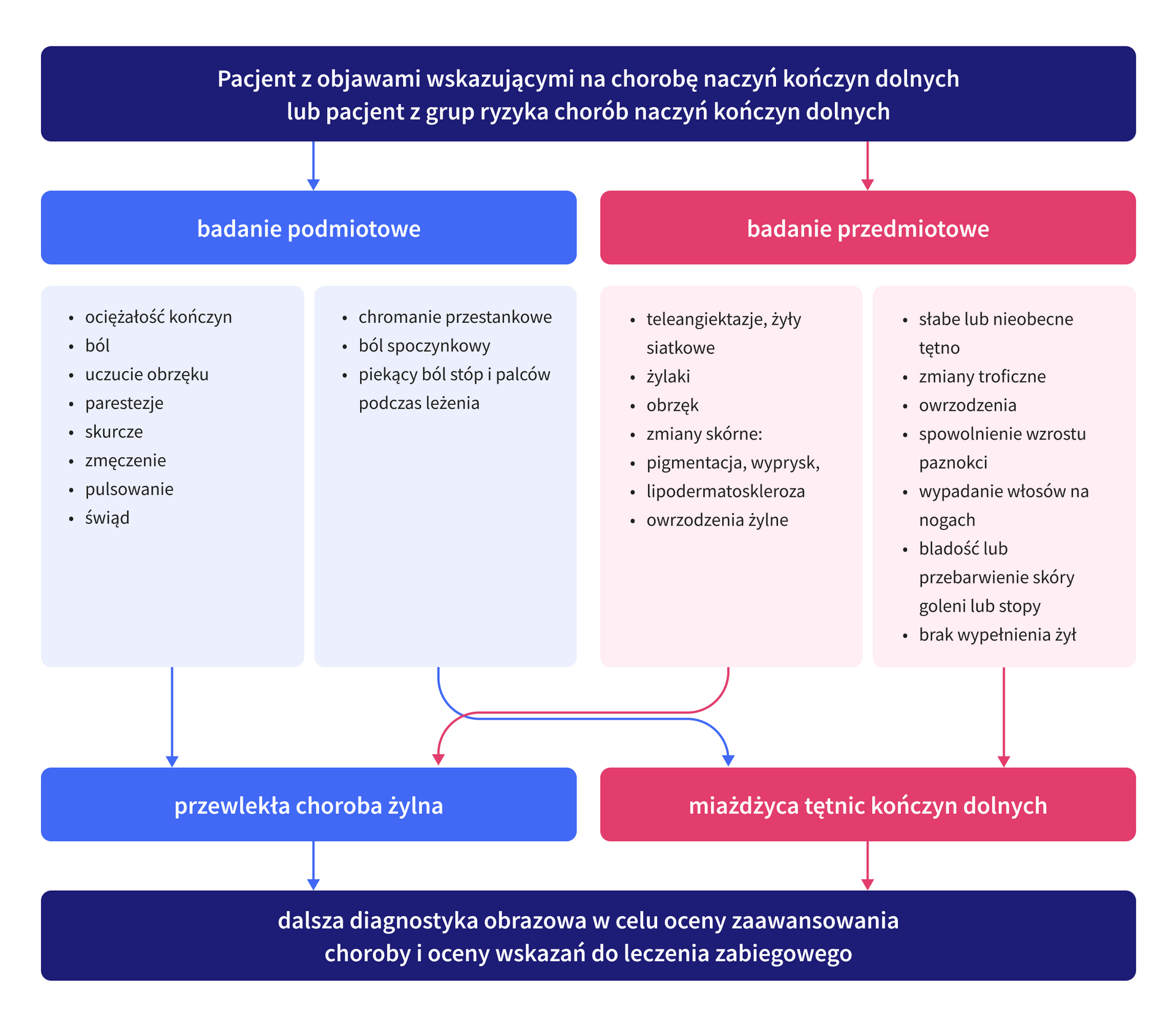
Podstawą diagnostyki PAD i CVD jest wnikliwe badanie podmiotowe i przedmiotowe. Rycina 2. podsumowuje objawy podmiotowe i przedmiotowe, na podstawie których można rozpoznać choroby naczyń kończyn dolnych.
Ogólne zasady leczenia zachowawczego pacjentów z chorobami naczyń kończyn dolnych
Postępowanie zachowawcze u pacjentów z PAD i CVD obejmuje wielokierunkowe leczenie schorzeń współistniejących oraz leczenie mające na celu poprawę jakości życia i poprawę rokowania.
Należy podkreślić, że skuteczna terapia PAD i CVD to także leczenie schorzeń współistniejących, a tym samym uzyskanie i utrzymanie wartości docelowych lipidów, glikemii, ciśnienia tętniczego, kwasu moczowego oraz masy ciała, a także stosowanie rekomendowanych dawek leków wykazujących właściwości przeciwkrzepliwe i/lub przeciwpłytkowe.
W leczeniu zachowawczym schorzeń naczyń żylnych znaczenie mają:
- leki wenoaktywne,
- kompresjoterapia,
- drenaż ułożeniowy [12].
Ważne, by uwzględnić fakt, że zaawansowana PAD jest przeciwwskazaniem do zastosowania kompresjoterapii.
Leki wenoaktywne to szeroka grupa obejmująca substancje pochodzenia rodzinnego i syntetycznego, mająca na celu ograniczenie choroby żylnej i redukcję objawów. W leczeniu przeciwzakrzepowym pacjentów z PAD można zastosować:
- leki przeciwpłytkowe w monoterapii lub w terapii podwójnej,
- riwaroksaban w dawce naczyniowej z kwasem acetylosalicylowym,
- sulodeksyd w monoterapii lub w skojarzeniu z lekiem przeciwpłytkowym.
Wybór zależy od oceny ryzyka zdarzeń niedokrwiennych i ryzyka krwawienia. Rycina 3. przedstawia schemat leczenia zachowawczego pacjentów z przewlekłą chorobą żylną współistniejącą z miażdżycą tętnic kończyn dolnych.
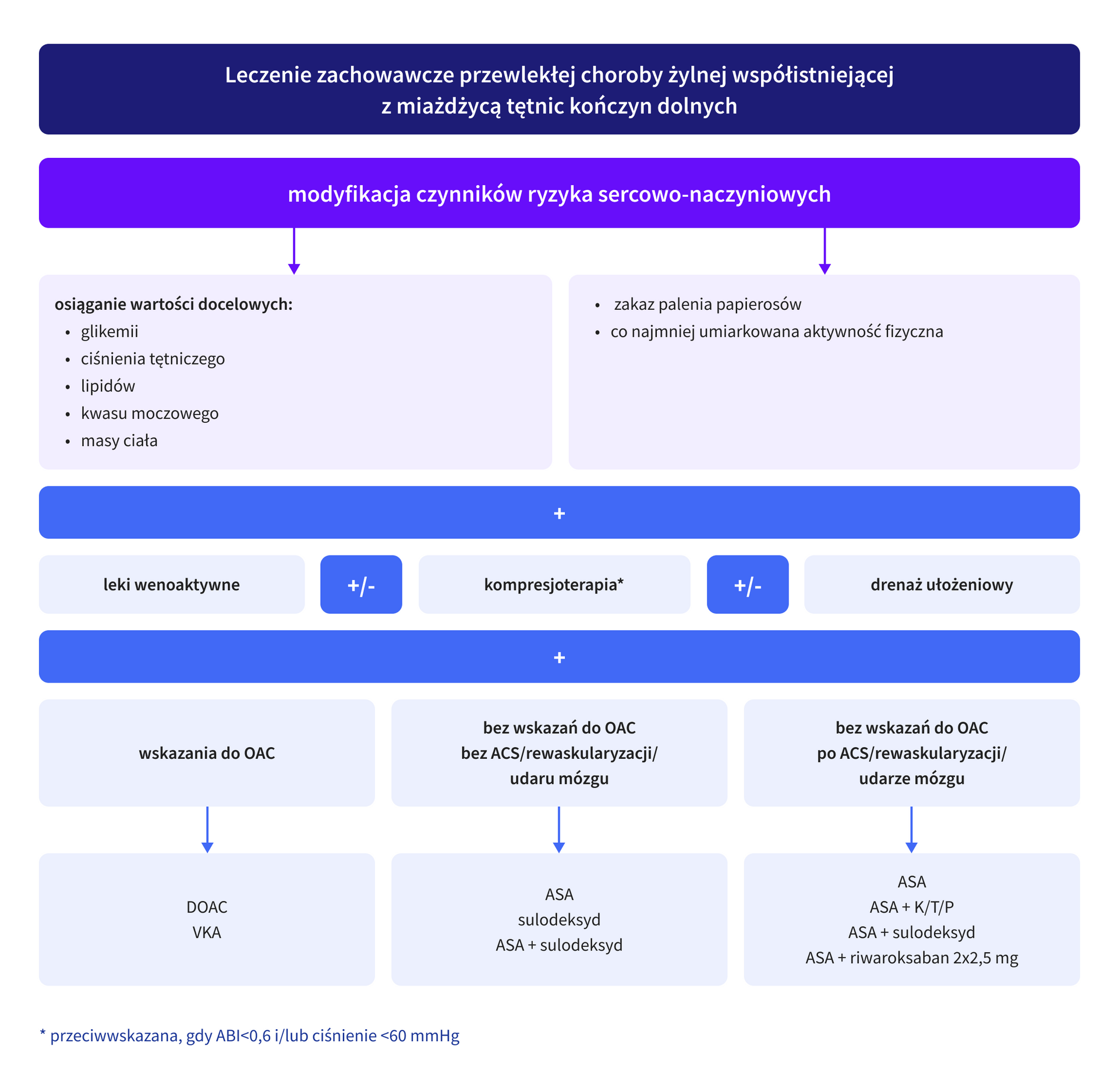
ASA – acetylsalicylic acid, kwas acetylosalicylowy; ACS – acute coronary syndrome, ostry zespół wieńcowy; DOAC – direct oral anticoagulant, bezpośredni doustny antykoagulant; K – klopidogrel; OAC – oral anticoagulant, doustny antykoagulant; P – prasugrel; T – tikagrelor; VKA – vitamin K antagonist, antagonista witaminy K
Sulodeksyd w leczeniu chorób naczyń kończyn dolnych
Sulodeksyd jest substancją, która łączy działanie przeciwzakrzepowe oraz wazoaktywne, stąd jest zalecany w leczeniu PAD i CVD [12].
W 80% składa się z cząsteczek heparyny o masie cząsteczkowej około 25 tys. daltonów, a w 20% z siarczanu dermatanu o masie cząsteczkowej około 7 tys. daltonów. Mechanizm przeciwzakrzepowego działania sulodeksydu jest złożony i obejmuje wielokierunkowe działanie, w tym hamowanie generacji trombiny, działanie profibrynolityczne oraz zmniejszenie generacji mikrocząstek o działaniu prokoagulacyjnym. Hamowanie generacji trombiny zachodzi wielokierunkowo – frakcja heparynowa za pośrednictwem antytrombiny silnie hamuje w osoczu aktywny czynnik X i w mniejszym stopniu trombinę, a siarczan dermatanu nasila działanie kofaktora heparynowego II, który jest inhibitorem trombiny związanej z fibryną. Sulodeksyd wpływa modulująco na endogenny układ fibrynolityczny, prowadząc do wzrostu stężeń endogennego aktywatora plazminogenu oraz obniżenia stężeń inhibitora aktywatora plazminogenu [14,15].
Kluczowy dla poprawy funkcjonowania naczyń tętniczych i żylnych mechanizm działania sulodeksydu polega na poprawie morfologii i funkcji śródbłonka. Sulodeksyd regeneruje glikokaliks, który warunkuje prawidłową funkcję śródbłonka i odpowiada za odporność na uszkodzenia. Śródbłonek naczyniowy jest ośrodkiem łączącym krążące komórki krwi ze strukturami ściany naczynia, do których zalicza się macierz podśródbłonkową oraz komórki mięśni gładkich. Funkcjonalna rola śródbłonka i odporność na uszkodzenia są zapewnione przez pokrywający go glikokaliks zbudowany głównie z glikozaminoglikanów, który reguluje przepuszczalność i selektywność komórek śródbłonka. Wykazano, że stosowanie sulodeksydu prowadziło do pogrubienia warstwy glikokaliksu na powierzchni komórek z jednoczesnym zmniejszeniem przepuszczalności ściany naczynia dla albumin [16]. Działanie protekcyjne sulodeksydu w stosunku do glikokaliksu jest dwukierunkowe, wynika z dostarczania substratu do odnawiania jego struktury oraz blokowania aktywności degradujących ją enzymów, heparynazy i hialuronidazy, które rozkładają glikozaminoglikany będące głównym budulcem glikokaliksu [17].
Poza wymienionymi działaniami, sulodeksyd wykazuje także inne korzystne dla naczyń tętniczych i żylnych działania, do których zalicza się:
- korzystne działanie na profil lipidowy,
- działanie antyproliferacyjne,
- działanie przeciwzapalne,
- hamowanie aktywności metaloproteinaz.
Wpływ sulodeksydu na redukcję obrzęku kończyn dolnych u pacjentów z CVD oceniono w metaanalizie Bignamini i wsp. [18], w której uwzględniono 8 badań klinicznych obejmujących 1005 chorych, w tym 522 leczonych sulodeksydem przez 2 miesiące, a pozostałych przez 3 miesiące. Obserwowano istotną redukcję obrzęku kończyn dolnych w przebiegu CVD u pacjentów leczonych sulodeksydem. W innym badaniu oceniono za pomocą badania pletyzmograficznego współczynnik filtracji naczyń włośniczkowych, będący wykładnikiem stopnia przepuszczalności naczyń mikrokrążenia. W grupie pacjentów leczonych sulodeksydem przez co najmniej 30 dni istotnie nastąpiła redukcja wartości powyższego indeksu mikrokrążenia w stosunku do wartości wyjściowych oraz w stosunku do pacjentów, u których stosowano placebo [19].
Z uwagi na plejotropowe działanie sulodeksydu, w tym przeciwkrzepliwe i profibrynolityczne, hamowanie reakcji zapalnej, ochronne działanie na śródbłonek, ale również działanie lipolityczne poprzez zwiększenie aktywności lipazy lipoproteinowej oraz działanie naczyniorozszerzające związane z indukcją produkcji tlenku azotu przez komórki śródbłonka naczyniowego tętnic, lek ten znajduje zastosowanie w leczeniu miażdżycowej choroby tętnic kończyn dolnych. W metaanalizie 6 badań wykazano istotne wydłużenie maksymalnego dystansu chodzenia o średnio 316 metrów. W badaniach, w których ujęto grupę kontrolną, stosowanie sulodeksydu powodowało istotnie statystycznie 2,4-krotnie wydłużenie maksymalnego dystansu chodzenia w porównaniu z grupą kontrolną [20]. Coccheri i wsp. [21] objęli badaniem 286 chorych z PAD w II stopniu niedokrwienia według klasyfikacji Fountaine. Pierwotnym punktem końcowym było wydłużenie dystansu chodzenia bez bólu o 100%, które uzyskano u 23,8% chorych stosujących sulodeksyd oraz u 9,1% chorych otrzymujących placebo (p=0,001). Wydłużenie dystansu chromania bez bólu po 27 tygodniach stosowania leku wyniosło średnio 83,2 ± 8,6 m (+64,7% w stosunku do wartości wyjściowych dla grupy leczonej sulodeksydem) oraz 36,7 ± 6,2 m (+29,9% w stosunku do wartości wyjściowych dla grupy placebo), p=0.001. W badanej grupie cukrzycę stwierdzono u 25% pacjentów, ale nie zaobserwowano różnic w grupie pacjentów z cukrzycą i bez cukrzycy. W metaanalizie obejmującej 11 badań oceniono wpływ sulodeksydu na dystans chromania przestankowego. Po 90 dniach stosowania leku stwierdzono wydłużenie dystansu chromania przestankowego o 68,9 ± 11,9 m [22].
Sulodeksyd wykazuje także korzystny wpływ na gojenie ran u pacjentów ze zmianami miażdżycowymi kończyn dolnych i cukrzycą. W grupie pacjentów leczonych sulodeksydem wykazano przyspieszenie gojenia owrzodzeń o 27 dni (95% CI 23–31 dni) oraz zwiększenie szansy na całkowite wygojenie [1,8 razy w porównaniu z grupą kontrolną (95% CI 1,4–2,4)] [18].
Należy podkreślić, że sulodeksyd jest lekiem o udowodnionym korzystnym wpływie na rokowanie pacjentów. Condorelli i wsp. [23] ocenili w randomizowanym badaniu wpływ sulodeksydu na śmiertelność w grupie pacjentów po zawale serca. Do badania włączono 3986 pacjentów po zawale serca otrzymujących standardową terapię lub standardową terapię z dołączonym sulodeksydem (600 LRU 1 × dziennie i.m. przez miesiąc, następnie 2 × dziennie doustnie 500 LRU). W rocznej obserwacji stwierdzono istotne statystycznie 32% zmniejszenie ryzyka zgonu oraz zmniejszenie ryzyka ponownego zawału serca o 28%.
W metaanalizie 6 badań obejmującej 7596 chorych ze średnim czasem obserwacji 11,6 miesiąca oceniono wpływ sulodeksydu na rokowanie długoterminowe. Badaniami włączonymi do metaanalizy objęto chorych z szerokim spektrum chorób naczyniowych, w tym pacjentów po ostrej fazie zawału serca, z przewlekłym niedokrwieniem kończyn dolnych oraz stabilnym dystansem chromania, pacjentów po epizodzie żylnej choroby zakrzepowo-zatorowej, chorych z cukrzycą i towarzyszącą mikro- i makroalbuminurią [24]. Wykazano, że sulodeksyd zmniejszał całkowitą śmiertelność (OR 0,67, 95% [CI 0,52–0,85], p=0,001) badanej populacji, jak również zmniejszał śmiertelność z przyczyn sercowo-naczyniowych (OR 0,44, [95% CI: 0,22–0,9], p=0,02). Ponadto odnotowano także zmniejszenie ryzyka wystąpienia zawału serca (OR 0,70 [95% CI: 0,51–0,96], p=0,03) oraz ryzyka nawrotu żylnej choroby zakrzepowo-zatorowej [OR 0,44 (95% CI: 0,24–0,81), p=0,008] [24].
Sulodeksyd jest lekiem, który ma zarejestrowane wskazanie w leczeniu chorób naczyń tętniczych i żylnych (tabela 2.).
Tabela 2. Praktyczne aspekty stosowania sulodeksydu.
| wskazanie | dawkowanie |
|---|---|
leczenie objawowe pierwotnej i wtórnej przewlekłej niewydolności żylnej | 2 x 2 kaps/dobę |
leczenie objawowe przewlekłej obturacyjnej choroby tętnic kończyn dolnycho umiarkowanym nasileniu (II stopień klasyfikacji Fontaine`a) | 2 x 2 kaps/dobę |
zastosowanie leku w praktyce | |
dawka leku a funkcja nerek | niezależna |
dawka leku a masa ciała | niezależna |
metabolizm | wątrobowy |
wydalanie | nerkowe |
monitorowanie parametrów układu krzepnięcia | nie dotyczy |
Z praktycznego punktu widzenia stosowanie sulodeksydu jest proste, dawka jest stała i nie wymaga modyfikacji. Sulodeksyd po podaniu doustnym wchłania się na całej długości przewodu pokarmowego. Pierwszy szczyt stężenia leku we krwi jest osiągany po dwóch godzinach, a drugi – między 4. a 6. godziną od podania. Między 6. a 12. godziną po podaniu sulodeksydu nie jest on wykrywany w osoczu. Ponownie pojawia się po 12 godzinach od podania i utrzymuje się do około 48 godzin. Te właściwości farmakokinetyczne wynikają z powolnego wtórnego uwalniania leku z narządów, przez które jest wychwytywany, a więc głównie ze śródbłonka naczyniowego. Dystrybucja leku jest szeroka, po podaniu doustnym sulodeksyd początkowo jest w komórkach jelitowych, następnie w kompartmencie centralnym, a potem w narządach miąższowych: mózgu, nerkach, sercu, płucach, jądrach. Objętość dystrybucji wynosi około 70 l. Metabolizm leku odbywa się w wątrobie. Wydalanie następuje głównie przez nerki (blisko 60% podanej dawki wydala się z moczem w ciągu 96 h) [25]. Tabela 3. przedstawia zasady stosowania sulodeksydu z innymi lekami.
Tabela 3. Stosowanie sulodeksydu z innymi lekami.
| Sulodeksydmożna stosować z: | Sulodeksydunie należy stosować z: |
|---|---|
ASA | ASA z klopidogrelem |
klopidogrelem | heparynami |
innymi lekami wenoaktywnymi | apiksabanem |
dabigatranem | |
riwaroksabanem |
ASA – acetylsalicylic acid, kwas acetylosalicylowy
Podsumowanie
Współistnienie chorób naczyń tętniczych i żylnych kończyn dolnych wynika ze wspólnego patomechanizmu obu schorzeń. Rozpoznanie CVD i PAD można postawić na podstawie badania podmiotowego i przedmiotowego, choć wykonanie dalszych badań jest niezbędne do oceny zaawansowania chorób i ustalenia wskazań do leczenia zabiegowego. U pacjentów, u których występuje jednocześnie CVD i PAD, sulodeksyd jest optymalnym rozwiązaniem, ponieważ wykazuje plejotropowe działanie w naczyniach tętniczych i żylnych.
Źródła
- Milusev, A., Rieben, R., & Sorvillo, N. (2022). The Endothelial Glycocalyx: A Possible Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disorders. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 9, 897087. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.897087
- Moore, K. H., Murphy, H. A., & George, E. M. (2021). The glycocalyx: a central regulator of vascular function. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology, 320(4), R508–R518. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00340.2020
- Salim, S., Machin, M., Patterson, B. O., Onida, S., & Davies, A. H. (2021). Global Epidemiology of Chronic Venous Disease: A Systematic Review With Pooled Prevalence Analysis. Annals of surgery, 274(6), 971–976. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004631
- Jawien A. (2003). The influence of environmental factors in chronic venous insufficiency. Angiology, 54 Suppl 1, S19–S31. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003319703054001S04
- Urbanek, T., Dorobisz, A., Gabriel, M., Hendiger, W., Jawień, A., & Kucharzewski, M. et al. (2015). Assessment of public awareness in the field of epidemiology, prevention and treatment of chronic venous diseases in Poland. Phlebological Review, 23(2), 45-53. https://doi.org/10.5114/pr.2015.54035
- Pannier-Fischer, F., Bromen, K., Schuldt, K., Stang, A., Poncar, C., Wittenhorst, M., Bock, E., Weber, S., Jöckel, K., & Rabe, E. (2003). Bonner Venenstudie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Phlebologie. Phlebologie, 32(01), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1617353
- Hiatt W. R. (2001). Medical treatment of peripheral arterial disease and claudication. The New England journal of medicine, 344(21), 1608–1621. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200105243442108
- Regensteiner, J. G., & Hiatt, W. R. (2002). Current medical therapies for patients with peripheral arterial disease: a critical review. The American journal of medicine, 112(1), 49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9343(01)01034-8
- Prochaska, J. H., Arnold, N., Falcke, A., Kopp, S., Schulz, A., Buch, G., Moll, S., Panova-Noeva, M., Jünger, C., Eggebrecht, L., Pfeiffer, N., Beutel, M., Binder, H., Grabbe, S., Lackner, K. J., Ten Cate-Hoek, A., Espinola-Klein, C., Münzel, T., & Wild, P. S. (2021). Chronic venous insufficiency, cardiovascular disease, and mortality: a population study. European heart journal, 42(40), 4157–4165. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab495
- Ammermann, F., Meinel, F. G., Beller, E., Busse, A., Streckenbach, F., Teichert, C., Weinrich, M., Neumann, A., Weber, M. A., & Heller, T. (2020). Concomitant chronic venous insufficiency in patients with peripheral artery disease: insights from MR angiography. European radiology, 30(7), 3908–3914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-06696-x
- Raffetto J. D. (2018). Pathophysiology of Chronic Venous Disease and Venous Ulcers. The Surgical clinics of North America, 98(2), 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2017.11.002
- Writing Committee Members, Gornik, H. L., Aronow, H. D., Goodney, P. P., Arya, S., Brewster, L. P., Byrd, L., Chandra, V., Drachman, D. E., Eaves, J. M., Ehrman, J. K., Evans, J. N., Getchius, T. S. D., Gutiérrez, J. A., Hawkins, B. M., Hess, C. N., Ho, K. J., Jones, W. S., Kim, E. S. H., Kinlay, S., … Wilkins, L. R. (2024). 2024 ACC/AHA/AACVPR/APMA/ABC/SCAI/SVM/SVN/SVS/SIR/VESS Guideline for the Management of Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 83(24), 2497–2604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2024.02.013
- Jawień, A., Filipiak, K. J., Doroszko, A., Dzieciątkowski, T., Krasiński, Z., Szymański, F. M., & Terlecki, P. (2023). Kompleksowa opieka nad pacjentem z chorobą naczyń obwodowych tętnic i żył — rekomendacje zespołu ekspertów 2023. Acta Angiologica, 29(2), 1–60. https://doi.org/10.5603/aa.2023.0008
- Fiore, G., Baraldi, A., Gambarotta, G.C. (1992). Inhibition of plasminoagen activator (PAI-1) by sulodexide in post-thrombophlebotic patients. J Drug Invest. 3. 173–178.
- Coccheri S. (2014). Biological and clinical effects of sulodexide in arterial disorders and diseases. International angiology : a journal of the International Union of Angiology, 33(3), 263–274.
- Broekhuizen, L. N., Lemkes, B. A., Mooij, H. L., Meuwese, M. C., Verberne, H., Holleman, F., Schlingemann, R. O., Nieuwdorp, M., Stroes, E. S., & Vink, H. (2010). Effect of sulodexide on endothelial glycocalyx and vascular permeability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia, 53(12), 2646–2655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1910-x
- Masola, V., Onisto, M., Zaza, G., Lupo, A., & Gambaro, G. (2012). A new mechanism of action of sulodexide in diabetic nephropathy: inhibits heparanase-1 and prevents FGF-2-induced renal epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Journal of translational medicine, 10, 213. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-213
- Bignamini, A. A., Chebil, A., Gambaro, G., & Matuška, J. (2021). Sulodexide for Diabetic-Induced Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Advances in therapy, 38(3), 1483–1513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01620-1
- Cospite, M., Ferrara, F., Cospite, V., & Palazzini, E. (1992). Sulodexide and the microcirculatory component in microphlebopathies. Current medical research and opinion, 13(1), 56–60. https://doi.org/10.1185/03007999209115223
- Shu, J., Zeng, L. Y., Lin, K. Y., Mu, P. W., Zhang, G. C., Chen, Y. M., & Wang, M. M. (2009). Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = Journal of Southern Medical University, 29(4), 778–780.
- Coccheri, S., Scondotto, G., Agnelli, G., Palazzini, E., Zamboni, V., & Arterial Arm of the Suavis (Sulodexide Arterial Venous Italian Study) group (2002). Sulodexide in the treatment of intermittent claudication. Results of a randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled study. European heart journal, 23(13), 1057–1065. https://doi.org/10.1053/euhj.2001.3033
- Gaddi, A. V., Capello, F., Gheorghe-Fronea, O. F., Fadda, S., & Darabont, R. O. (2020). Sulodexide improves pain-free walking distance in patients with lower extremity peripheral arterial disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JRSM cardiovascular disease, 9, 2048004020907002. https://doi.org/10.1177/2048004020907002
- Condorelli, M., Chiariello, M., Dagianti, A., Penco, M., Dalla Volta, S., Pengo, V., Schivazappa, L., Mattioli, G., Mattioli, A. V., & Brusoni, B. (1994). IPO-V2: a prospective, multicenter, randomized, comparative clinical investigation of the effects of sulodexide in preventing cardiovascular accidents in the first year after acute myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 23(1), 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-1097(94)90498-7
- Bikdeli, B., Chatterjee, S., Kirtane, A. J., Parikh, S. A., Andreozzi, G. M., Desai, N. R., Francese, D. P., Gibson, C. M., Piazza, G., Goldhaber, S. Z., Eikelboom, J. W., Krumholz, H. M., & Stone, G. W. (2020). Sulodexide versus Control and the Risk of Thrombotic and Hemorrhagic Events: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Seminars in thrombosis and hemostasis, 46(8), 908–918. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1716874


